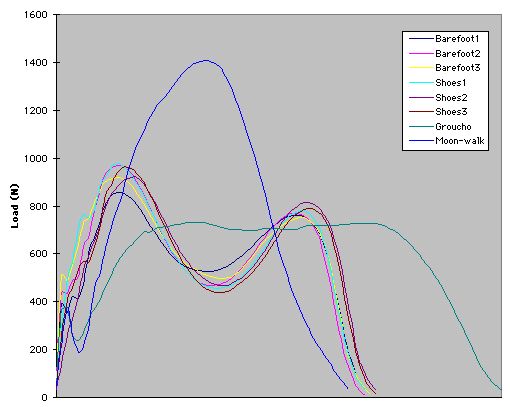
It is clear from the above that the ground reaction forces reflect accelerations of the body's centre of mass. They are not, as many wrongly people believe, influenced by changes in footwear. This is illustrated in the following set of curves taken from a subject walking three times barefoot and shod, then walking like Groucho Marx (minimal vertical accelerations) and as if on the moon (large vertical accelerations).

It can be seen that there are no significant differences in the curves according to footwear, but considerable differences when trunk accelerations are modified.
I came across your theory of the "Origin of ground reaction forces"
while
searching for somewhat similar data.
I am an engineer at Blue Giant. We manufacture material handling
equipment
used in factories and warehouses. One of our products is a mechanical
dock
leveler that bridges the gap between a tractor-trailer and the factory
floor. The ramp is mechanically raised by the use of springs
under the
dock. A lip then extends to bridge the gap. Personnel must
walk up the
ramp in order to bring the lip down to the truck bed. When doing
this they
must overcome the strength of extension springs under the dock.
Sometimes a lighter person has trouble forcing the deck downwards because
they are not heavy enough. They must walk further along the dock
and
sometimes bounce downward to get it moving downward. They should
never be
jumping, but what they do is bend their knees quickly, producing a
slight
acceleration of their upper body, and hence more force on the dock.
I am
having trouble determining the force somebody can produce by performing
this
motion. We have a scale that I have bounced on but the response
time is not
good enough to get a proper reading of force. Reading your reaction
forces
article, it seems as though you might have or be able to direct me
to, info
on producing a force greater than your body mass by quickly bending
at the
knees.
You can call by phone or e-mail me.
Thank-you for your consideration.
Andy Erjavec
Blue Giant Limited
1-800-668-7078
ext 291
I have been trying to interpret the GRF tracings during the stance phase
of gait and have found
what appears to be conflicting information from the CGA website.
I will do my best to present this information as clearly and completely as possible.
In your "The origins of ground reaction forces" /faq/grfs.html,
it states the following:
An upwards acceleration (as occurs at push-off) will be reflected in an
increase in the vertical load (weight) recorded, while a downwards
acceleration (as occurs
during mid-stance) will reduce the effective body weight.
I am not clear regarding the downward acceleration occurring at midstance,
that would evidently
be the source of the reduced bodyweight and the midstance valley.
In an additional CGA posting, from Kinematic Definitions, it states
and there is an
illustration that represents the fact that the COM actually moves upwards
during midstance and
is higher in midstance than anywhere else during the normal gait cycle.
(
/teach-in/kinematics.html)
I seem to have difficulty trying to reason this out, (it probably should
not be that
difficult), yet I continue to struggle. Any information that
would help me clear this up and
assist in my understanding of these GRF's would be greatly appreciated.
In addition, I have
looked for textbooks that explain the use and interpretation of force
plates but have not been
satisfied with what I have found. A few that I have looked through
are Perry, Whittle,
Durward, and several general Biomechanics textbooks. Are there
any texts that you would
recommend?
Thank you for your time in addressing these issues.
Dear Kurt,
No discrepancy - you're just getting mixed up between position and
acceleration. Displacement, velocity and accelerarion are always 90
degrees out of phase. Velocity is the slope of the displacement, and
acceleration the slope of the velocity. Think of it in stages (see
attached fig.):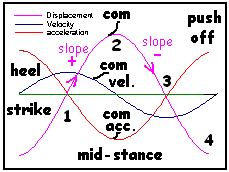
1. When displacement is rising
2. When displacement is highest
3. When displacementis falling
4. When displacement is lowest
Chris
Bergman , G., Kniggendorf, H., Graichen, F.
and Rohlmann, A.
(1995) Influence of shoes and heel strike
on the loading of the hip
joint. J. Biomechanics 28:817-827.
Cavanagh, P. R. and Lafortune, M. A. (1980)
Ground reaction forces
in distance running. J. Biomech. 13, 397-406.
Cavanagh, P.R. (1978) A technique for averaging
centre of
prepssure paths from a force platform. J.
Biomech 11: 487-491.
Cavanagh, P.R., Williams, K.R., and Clarke,
T.E. (1981) A
comparison of ground reaction forces during
walking barefoot and in
shoes. pp151-156 in Morecki et al (Eds) Biomechanics
VII-B,
University Park Press.
Chu., M.L., Yasdani-Ardakani, S. Gradisar,
I.A. & Askew, M.J.
(1986) An in vivo simulation study of impulsive
force transmission
along the lower skeletal extremity. J. Biomech
19:979-987
Clarke, T.E., Cooper, L.B. , Clark, D.E. &
Hamill, C.L. (1985) The
effect of increased running speed upon peak
shank deceleration
during ground contact. Pp 101-105 in. Winter
et al (Eds)
Biomechanics IX-B, Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics.
Clarke, T. E., Frederick, E. C. and Cooper,
L. B. (1983b) Effects of
shoe cushioning upon ground reaction forces
in running. Int. J.
Sports Medicine 4:247-251.
Cole, G.K., Nigg. B.M., Fick, G.H and Morlock, M. M. (1995) Internal loading of the foot and ankle during impact in running. J. Applied Biomechanics 11: 25-46.
Dickinson, J.A., Cook, S.D. & Leinhardt
T.M. (1985) The
measurement of shock waves following heel
strike during running J.
Biomech 18: 415-422.
Frederick, E.C. and Hagy J. L.(1986) Factors
effecting peak vertical
ground reaction forces in running. Int. J.
Sports Biomech. 2: 41-49
Hamill, J., Bates, B.T., Knutzen, K.M. and
Sawhill, J.A. (1983)
Variations in ground reaction force parameters
at different running
speeds. Human Movement Science, 2: 47- 56.
Hamill, J., Bates, B.T., & Knutzen, K.M.
(1984) Ground reaction
force symmetry during walking and running.
Research Quarterly,
55:289-293.
Falsetti, H.L., Burke, E.R. Feld, R.D., Frederick,
E.C. and Ratering,
C. (1983) Hematological variations after endurance
running with hard
and soft-soled shoes. Physician and Sportsmedicine
11(8):118-127
Hennig, E.M. & Lafortune, M.A. (1988) Tibial
bone and skin
accelerations during running. In C.E. Cotton
et al (Eds) Proc 5th
Biennial Conf. And Human Locomotion Symposium
of the Canadian
Society of Biomechanics (pp 94-95) Ottowa:
University of Ottowa,
Dept. Kinanthropometry.
Hennig, E.M. & Lafortune, M.A. (1991) Relationships
between
ground reaction force and tibial acceleration
parameters. Int. J.
Sports Biomech 7: 303-309.
Lafortune, M.A. (1991) Three-dimensional acceleration
of the tibia
during walking and running. J. Biomechanics
24: 877-886.
Lafortune, M.A., Lake, M.J. and Hennig, E.M.
(1995) Transfer
function between tibial acceleration and ground
reaction force. J.
Biomechanics 28:113-117.
Lafortune, M.A. & Hennig, E.M. (1988) Effects
of velocity and uphill
slope on tibial shock during running. In C.E.
Cotton et al (Eds) Proc
5th Biennial Conf. And Human Locomotion Symposium
of the
Canadian Society of Biomechanics (pp 74-75)
Ottowa: University of
Ottowa, Dept. Kinanthropometry.
Lafortune, M.A. & Hennig, E.M. (1989) Contribution
of angular
motion and gravity to tibial acceleration
. In R.J. Gregor et al (Eds)
Proc XII international Congress of Biomechanics.
Los Angeles,
UCLA, Dept of Kinesiology #334.
Lafortune, M.A. & Hennig, E.M. (1992) Cushioning
properties of
footwear during walking: accelerometer and
force platform
measurements. Clinical Biomechanics 7: 181-184.
Light, L.H., McLellan, G.E. and Klenerman,
L. (1980) Skeletal
transients on heel strike in normal walking
with different footwear. J.
Biomechanics 13: 477-480.
Luethi, S.M., Nigg, B.M. and Bahlsen, H.A.
(1984) The influence of
varying shoe sole stiffnesses on impact forces
in running. in Human
Locomotion III, Proceedings of the 1984 Conference
of the
Canadian Society of Biomechanics.
MacLellan, G.E. & Vyvyan, B. (1981) Management
of pain beneath
the heel and Achilles tendonitis with viscoelastic
heel inserts.. Brit. J.
Sports Medicine 15, 117-121.
Ziegert , J.C. and Lewis, J.L (1979) The effect
of soft tissues on
measurements of vibrational bone motion by
skin-mounted
accelerometers.
Frederick, E.C., Howley, E. T., Hamill, C.L. and Cooper. L.B. (1984) Ventilatory contributions to shock attenuation. Med. Sci. Sports. Ex. 16: 185.
Munro, C.F., Miller, D.I. and Fugevand, A.J.
(1987) Ground reaction
forces in running. A reevaluation. Journal
of Biomechanics 20:
147-155.
Nachbauer, W. & Nigg, B.M (1992) Effects
of arch height of the foot
on ground reaction forces in running. Med
Sci Sports Ex
24:1264-1269. Nigg, B.M. (Ed) (1986) Biomechanics
of Running
Shoes. Champaign IL, Human Kinetics.
Nigg, B.M., Bahlsen, H.A. Luethi, S.M., and
Stokes, S. (1987) The
influence of running velocity and midsole
hardness on external
impact forces in heel-toe running. Journal
of Biomechanics 20:
951-959.
Nigg, B.M., Herzog, W. and Read J.L. Effect
of viscoelastic shoe
insoles on vertical impact forces in heel-toe
running. Am. J. Sports
Med. 16:70-76.
Noe, D.A., Voto, S.J., et al, (1993) Role of
the calcaneal heel pad
and polyumeric shock absorbers in attenuation
of heel strike impact.
J. Biomed Engng 15: 23-26.
Oakley, T. And Pratt, D.J.. (1988) Skeletal
transients during heel and
toe strike running and the effectiveness of
some materials in their
attenuation. Clinical Biomecahnics, 3: 159-165.
Valiant G.A., McMahon, T.A. and Frederick,
E.C. (1987) A new test
to evaluate the cushioning properties of athletic
shoes. In B.
Jonsson (Ed) Biomechanics X-B (pp 937-941).
Champaign, IL,
Human Kinetics.
Voloshin,A.S., Burger, C.P. et al: (1985) An
in-vivo evaluation of the
leg's shock absorbing capacity. In Winter
et al (Eds) Biomechanics
IX-B (pp 112-116) Champaign, IL., Human Kinetics.
Voloshin, A.S. and Wosk, J. (1982) An in-vivo study of low back pain and shock absorption in the human locomotor system. J. Biomechanics 15, 21-27.
Wosk, J. & Voloshin, A.S. (1981) Wave attenuation
in the skeletons
of young heallthy persons. J. Biomechanics
14:261-267
Cavanagh, P.R. and Ae, M. (1980) A technique
for the display of
pressure distribution data beneath the foot.
J. Biomech 13:69-75.
Cavanagh, P.R. and Hennig E.M. (1982) A new
device for the
measurement of pressure distribution on a
rigid surface. Med. Sci
Sports Ex. 14: 153p
Hennig, E.M and Rosenbaum, D. (1991) Pressure
distribution under
the feet of children in comparison with adults.
Foot and Ankle
11:306-311.
Hennig, E.M., Cavanagh, P.R. and Macmillan,
N.H. (1983) Pressure
distribution easurements by high precision
piezo-ceramic force
transducers. pp 1081-1088 in H. Matsui and
K. Kobayashi (Eds)
Biomechanics VII-B, Champaign, IL, Human Kinetics.
Hennig, E.M., Valiant G.A. & Liu,Q. (1993)
Relationships between
perception of cushioning and pressure distribution
parameters in
running shoes. Pp564-565 in Bioouisett et
al (Eds) Biomechanics
XIV Paris: International Society of Biomechanics.
Shorten, M.R., Eden, K.B and Himmelsbach, J.A.
(1989) Plantar
pressure distribution during barefoot walking.
Proc XII International
Congress of Biomechanics (Edited by Gregor,
R. J., Zernicke, R. F.
and Whiting, W. C.), #120. Department of Kinesiology,
UCLA, Los
Angeles, Ca.
Shorten, M. R. and Winslow, D. S. (1989) Multiple
element model of
running shoe cushioning. Proc 13th Ann. Meeting
Am. Soc.
Biomech., pp. 88-89. University of Vermont,
Burlington, Vt.
Shorten, M.R. and Winslow D.S.(1992) Spectral
analysis of impact
shock during running. Int. J. Sports Biomechanics
8:288-304
Smeathers, J.E. (1989) Measurement of transmissibility
for the
human spine during walking and running. Clinical
Biomechanics 4:
34-40.
Snel, J. G., Delleman, N. J., Heerkens, Y.
F. and van Ingen Schenau,
G. J. (1985) Shock absorbing characteristics
of running shoes during
actual running. Biomechanics IX-B (Edited
by Winter, D. A., Norman,
R. W., Wells, R. P., Hayes, K. R. and Patla,
A. E.), pp. 133-137.
Human Kinetics Publ, Champaign, Il.
Alexander, R. McN. and Bennet Clark, H. C. (1977) Storage of strain energy in muscles and other tissues. Nature, Lond. 265, 114-117.
Bennett, M.B. and Ker, R.F. (1990) The mechanical
properties of the
human subcalcaneal fat pad in compression.
J. Anatomy. 171:
131-138.
Bojsen-Moeller, F. (1978) The human foot, a
two speed
construction. pp 261-266 in Asmussen E. and
Jorgensen, K. (Eds)
Biomechanics VI-A., Baltimore, IL, University
Park Press.
Bojsen-Moeller, F. (!979) Calcaneocuboid joint
and stability of the
longitudinal arch of the foot at high gear
and low gear push-off. J.
Anatomy, 129:165-176
De Clercq, D. Aerts, P and Kunnen, M. (1994)
The mechanical
characteristics of the human heel pad during
foot strike in running: an
in vivo cineradiographics study. J. Biomechanics
27: 1213-1222.
Ker, R. F., Bennett, M. B., Bibby, S. R., Kester, R. C. and Alexander, R. McN. (1987) The spring in the arch of the human foot. Nature, Lond. 325, 147-149.
Hawes, M.R. and Sovak, D. (1994) Quantitative
morphology of the
human foot in a North American population.
Ergonomics
37:1213-1226.
Holden J.P., Cavanagh, P.R., Williams, K.R.,
and Bednarski, K.R.
(1983). Foot angles during walking and running.
In D.A. Winter, R.W. Norman, R.P. Wells, K.C. Hayes and A.E. Patla (Eds.),
Biomechanics IX-A, 451-457, Champaign, IL:
Human Kinetics
Publishers, Inc.
Inman, V.T. (1976). The joints of the ankle.
Baltimore: Williams and
Wilkins Co.
Kernozek, T.W. and Ricard, M.D. (1990). Foot
placement angle and
arch type: effect on rearfoot motion. Archives
of Physical Medicine
and Rehabilitation, 71, 988-991.
Kinoshita, H. Ogawa, T., Kuzuhara, K. And Ikuta,
K. (1993) In vivo
examination of the dynamic properties of the
human heel pad. Int. J.
Sports Med. 14: 312-319.
McMahon, T.A. (1987) The spring in the human
foot. Nature, Lond.
325, 108-109.
Bates, B., Osternig L.R., Mason, B. and James,
S.L. (1978) Lower
extremity function during the support phase
of running. pp 30-39 in
Asmussen et al (Eds) Biomechanics VI-B, University
Park Press,
Baltimore.
Bates, B., Osternig L.R., Mason, B. and James,
S.L. (1979a) Foot
orthotic devices to modify selected aspects
of lower extremity
mechanics. Am J Sports Med 7:338-342
Bates, B., Osternig L.R., Mason, B. and James,
S.L. (1979b)
Functional variability of the lower extremity
during the support phase
of running. Med Sci Sports Ex. 11: 328-331.
Bauer, H. (1970) The effect of high top and
low cut football shoes on
speed and agility. Athletic Journal 50:74.
Clarke, T. E., Frederick, E. C. and Hamill,
C.L. (1983) The effects of
shoe design parameters on rearfoot control
during running. Med Sci
Sports Ex. 15:376-381.
Clarke, T.E., Frederick, E.C., and Hamill,
C.L. (1984). The study of
rearfoot movement in running. In E.C. Frederick
(Ed.), Sport shoes
and playing surfaces (pp. 166-189). Champaign,
IL: Human Kinetics
Publishers
Edington, C.J., Frederick. E.C. and Cavanagh,
P.R. (1990) Rearfoot
motion in distance running. pp 135-164 in
P.R. Cavanagh (Ed)
Biomechanics of distance running. Champaign,
IL, Human Kinetics.
Engsberg, J.R. (1987) A biomechanical analysis
of the talocalcaneal
joint - in vitro. J. Biomechanics 20: 429-
442. Engsberg, J.R. and
Andrews J.G. (1987) kinematic analysis of
the
talocalcaneal/talocrural joint during running
support. Med Sci Sports
Ex 19:169-184.
Cornwall, M.W. and McPoil, T.G. (1993) Reducing
2-dimensional
rearfoot motion variability during walking.
J. Am Podiatr Ass.
83:394-397.
Milani, T.L., Schnabel, G and Hennig, E.M.
(1995) Rearfoot motion
and pressure distribution patterns during
running in shoes with varus
and valgus wedges. J. Applied Biomechanics
11: 177-187.
D'Ambrosia, R., and Douglas, R. (1982). Orthotics.
In R.
D'Ambrosia and D. Drez (Eds.), Prevention
and treatment of running
injuries. New Jersey: Slade.
Ferrandis, R., Garcia, R., Ramira, J., Hoyos,
J and Vera, P. (1994)
Rearfoot motion and torsion in running: the
effects of upper vamp
stabilisers. J. Applied Biomechanics 10:28-42.
Hamill, J., Freedson, P.S., Boda, W., and Reichsman,
F. (1987).
Effects of shoe type on cardiorespiratory
responses and rearfoot
motion during treadmill running. Medicine
and Science in Sports and
Exercise, 20, 515-521.
Nigg, B.M and Bahlsen, H.A. (1988) Influence
of heel flare and
midsole construction on pronation, supination
and impact forces for
heel-toe running. Int. J. Sports Biomechanics
4:205-219.
Nigg, B.M., Luethi, S.M., Stacoff, A., and
Segesser, B. (1984).
Biomechanical effects of pain and sport shoe
corrections. The
Australian Journal of Science and Medicine,
16, 10-16.
Nigg, B.M and Morlock, M. (1987) The influence
of lateral heel flare
of running shoes on pronation and impact force.
Med. Sci Sports
Ex. 19: 294-301
Pope, M.H., Renstrom, P., Donnermeyer, D.,
and Morgenstern, S.
(1987). A comparison of ankle taping methods.
Medicine and
Science in Sports and Exercise, 19, 143-147.
Procter, P., Berme, N., and Paul, J.P. (1981).
Ankle joint
biomechanics. In A. Morecki, K. Fidelus, K.
Kedizor, and A. Wit
(Eds.), Biomechanics VII-A (pp. 52-56). Baltimore:
University Park
Press.
Quinn, T.P., Mote Jr., C.D., and Skinner, H.B.
(1991). The effect of
ankle constraint on the torsional laxity of
the knee during
internal-external rotation of the foot. Journal
of Biomechanics, 24,
511-525.
Reinschmidt, C., and Nigg, B.M. (1995) Influence
of heel height on
ankle joint moments in running. Med Sci Sports
Ex 27:410-416.
Rodgers, M.M. and LeVeau, B.F. (1982) Effectiveness
of foot
orthotic devices used to modify pronation
in runners. J. Orthopaedic
and Sports Physical Therapy. 4:86-90.
Robinson, J.R., Frederick, E.C. and Cooper,
L.B. (1986) Systematic
ankle stabilisation and the effect on performance.
Med Sci Sports
Ex 18: 625-628.
Smith, M., Clarke, T., Hamill, C. and Santopietro,
F. (1986) The
effect of soft and semi-rigid orthoses upon
rearfoot motion in
running. Podiatric Sports Medicine 76:227-233.
Stacoff, A., and Kaelin, X. (1983). Pronation
and sport shoe design.
In B.M. Nigg and B.A. Kerr (Eds.), Biomechanical
aspects of-sport
shoes and playing surfaces (pp. 143- 151).
Calgary: University
Printing. Stacoff, A.,
Stuessi, E. & Sondereger, D. (1983). Lateral
stability of sports
shoes. In Winter D.A. (Ed) Biomechanics IX,
Champaign, IL, Human Kinetics. Stacoff, A., Denoth, J., Kaelin, X.,
Stacoff, A., Kaelin, X., Stuessi, E. and Segesser,
B. (1989) The
torsion of the foot in running. Int. J. Sports
Biomechanics. 5:
375-389.
Stacoff, A., Kaelin, X. and Stuessi, E. (1991)
The effects of shoes
on torsion and rearfoot motion in running.
Med Sci Sports Ex.
23:482-490. Sousas-Little, R.W., Beavis G.C.,
Verstraete, M.C. & Markus, T.L. (1987)
Analysis of foot motion
during running using a joint coordinate system.
Medicine and
Science in Sports and Exercise 19:285-293.
Vagenas, G., and Hoshizaki, B. (1988). Evaluation
of rearfoot
asymmetries in running with worn and new running
shoes.
International Journal of Sports Biomechanics
, 4, 220- 230.
Van Gheluwe, B., Tielemans, R. and Roosen,
P. The influence of
heel counter rigidity on rearfoot motion during
running. J. Applied
Biomechanics 11:47-67.
Williams, K.R. (1982). Non-saggital plane movements
and forces
during distance running. Proceedings of the
Sixth Annual Conference
of the ASB.
Morehouse, C.A. and Niebel, B.W. (1975) Torques
developed by
different types of shoes on various playing
surfaces. Med Sci
Sports Ex. 7:127-131.
Perkins, P.J. and Wilson, M.P., Slip resistance
testing of shoes -
new developments. Ergonomics 26:73-82.
Rheinstein, D.J., Morehouse, C.A. and Niebel,
B.W. Effects on
traction of outsole composition and hardnesses
of basketball shoes
and three types of playing surfaces. Med Sci
Sports Ex 10:282-288.
Unold, E. and Nigg, B.M. (1983) The frictional
characteristics of
tennis shoes. pp153-160 in Nigg, B.M and Kerr,
B.A (Eds)
Biomechanical aspects of sports shoes and
playing surfaces.
University Printing, Calgary.
Valiant G.A. (1986) The effect of outsole pattern
on basketball shoe
traction. Pp 29-37 in J. Terauds (Ed) Biomechanics
in Sports III &
IV. DelMar, CA, Academic Publishers.
Valiant, G.A. (1988) Ground reaction forces
developed on artificial
turf. pp 406-415 in Science and Football (Ed
T. Reilly et al ) London,
E.&F.N. Spon.
Valiant, G.A. (1989) Transmission and attenuation
of heel strike
accelerations. Pp 225-247 in P.R. Cavanagh
(Ed) The biomehanics
of distance running. Champaign, IL.. Human
Kinetics.
Valiant, G.A. and Cavanagh, P.R. (1983) A study
of landing from a
jump: implications for the designj of a basketball
shoe. In Winter D.A
(Ed) Biomechanics IX, Champaign, IL, Human
Kinetics.
Torg J.S. and Quedenfeld T.C. (1971) Effect
of shoe type and cleat
length on the incidence and severity of knee
injuries among
Philadelphia High School football players.
Res Quart 42:203-211.
Van Gheluwe, B., Deporte, E. and Hebbelinck,
M. Frictional forces
and torques of soccer shoes on artificial
turf. pp161-168 in Nigg,
B.M and Kerr, B.A (Eds) Biomechanical aspects
of sports shoes
and playing surfaces. University Printing,
Calgary.
Alexander, R. McN.(1988) The spring in your
step: the role of elastic
mechanisms in human running. Biomechanics
XI-A (Edited by de
Groot, G., Hollander, A. P., Huijing, P. A.
and van Ingen Schenau, G.
J.), pp. 17-25. Free University Press, Amsterdam.
Alexander, R. McN. (1991) Energy-saving mechanisms
in walking
and running. J. exp. Biol. 160: 55-69.
Clement, D.B., Taunton, J.E. Wiley, J.P., Smart.
G.W. and
McNichol, K.L. (1982) Investigation of metabolic
efficiency in
runners with and without corrective orthotic
devices. Int. J. Sports
Med. 2: 14-15.
Frederick, E.C., Howley, E.T., and Powers,
S.K. (1980). Lower O2
cost while running on air cushion type shoe.
Medicine and Science in
Sports and Exercise, 12, 81-82.
Frederick, E. C., and Powers, S. K. (1986)
Lower oxygen demands
of running in soft soled shoes. Res. Quart.
Ex. Sport 57, 174-177.
Frederick, E. C., Clarke, T. E., Larsen, J.
L. and Cooper, L. B.
(1983) The effects of shoe cushioning on the
oxygen demands of
running. Biomechanical Aspects of Sports Shoes
and Playing
Surfaces (Edited by Nigg, B. M. and Kerr,
B. A.), pp. 107-114. The
University of Calgary, Calgary.
Glieck, J.A. (1987) Running shoes waste natural
energy of feet. New
York Times, June 2, 1987, p 19.
Hammill, J., Freedson, P.S., Boda, W., and
Reichsman, F. (1987).
Effects of shoe type on cardiorespiratory
responses and rearfoot
motion during treadmill running. Medicine
and Science in Sports and
Exercise, 20, 515-521.
Hayes, J., Smith, L., and Sanpietro, F. (1983).
The effect of
orthotics on the aerobic demands of running.
Medicine and Science
in Sports and Exercise, 15, 169.
Shorten, M. R. (1989) Elastic energy in athletic
shoe cushioning
systems. Proc. XII International Congress
of Biomechanics (Edited
by Gregor, R. J., Zernicke, R. F. and Whiting,
W. C.), #120.
Department of Kinesiology, UCLA, Los Angeles,
Ca.
Shorten, M. R. (1992) The Energetics of Running
and Running
Shoes. J. Biomechanics 26: S41-51.
Brubaker, C.E., and James, S.L. (1974). Injuries
to runners. Journal
of Sports Medicine, 2, 189-199.
Clement, D.B., Taunton, J.E., and Smart, G.W.
(1984). Achilles
tendinitis and peritendinitis: Etiology and
treatment. American
Joumal of Sports Medicine, 12, 179-184.
Clement, D.B., Taunton, J.E., Smart. G.W. and
McNichol, K.L.
(1981) A survey of overuse injuries in running.
Physician and
Sportsmedicine 9:47-58
Cox, J.S. (1985) Patellofemoral problems in
runners. Clinics in
Sports Medicine 4:699-715.
Detmer D.E. (1986) Chronic shin splints classification
and
management of medial tibial stress syndrome.
Sports Medicine 3:
436-446.
Jackson, D.W. (1978). Shinsplints: an update.
Physician Sports
Medicine, 6, 49-68.
James, S.L., Bates, B.T. and Osternig,. L.R.
(1978) Injuries to
runners. Am. J. Sports Medicine 6: 40-49.
Gardner, L.I et al (1988) Prevention of lower
extremity stress
fractures: a controlled trial of a shock absorbent
insole. Am J. Public
Health 78: 1563-1567.
Krissoff, W.B., and Ferris, W.D. (1979). Runner's
injuries. The
Physician and Sports Medicine, 7:12, 55-64.
Leach, R. (1982). Running injuries of the knee.
In R. D'Ambrosia and
D. Drez (Eds.), Prevention and treatment of
running injuries (pp.
55-75). New Jersey: Slade.
Marcus, B. (1983). The influence of footwear
and surfaces on
performance and injury potential in running.
Unpublished doctoral
dissertation. Imperial College, University
of London.
McKenzie, D.C. Clement, D.B. & Taunton,
J.D. (1985) Running
shoes, orthotics and injuries. Sports Medicine
2: 334- 337.
Messier, S.P. and Pittala, K.A. (1988) Etiologic
factors associated
with selected running injuries. Med Sci Sports
Ex. 20: 501-505.
Milgrom, C., Giladi, M, et al (1985) A prospective
study of the effect
of a shock absorbing orthotic device on the
incidence of stress
fractures in military recruits. Foot and Ankle
6: 101-104.
Miller, B.J., Pate R.R. and Burgess, W. (1988)
Foot impact force
and intravascular hemolysis during distance
running. Int. J. Sports
Medicine, 9: 56-60.
Smart, G.W., Taunton, J.E. and Clement, D.B.
Achilles tendon
disorders in runners: a review. Med Sci Sports
12: 231- 243.
Stuessi, E. (1988) Running injuries and shoe
construction: some
possible relationships. Int. J. Sports Biomech
4: 342-357.
Subotnick, S.I. (1979). Cures for common running
injuries. Mountain
View, CA:Anderson World, Inc.
Subotnick, S.I. (1980). The cavus foot. Physician
and Sports
Medicine, 8(7):53-55
Subotnick, S.I. (1981). The flat foot. Physician
and Sports Medicine,
9, 85-91.
Taunton, J.E., Clement, D.B. & McNichol,
K. (1982) Plantar fasciitis
in runners. Canadian J. Applied Sports Science
7:41-44.
Tiberio, D. (1987). The effect of excessive
sub-talar joint pronation
on patellofemoral mechanics : a theoretical
model. Journal of
Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, 9:160-165.
Other shoe characteristics
Caitlin, M.E., and Dressenhofer, R.F. (1979).
Effects of shoe weight
on the energy cost of running. Medicine and
Science in Sports and
Exercise, 11, 80.
Williams, K.R., and Ziff, J.L. (1991). Changes
in distance running
mechanics due to systematic variations in
running style. International
Journal of Sports Biomechanics, 7, 76-90.
McMahon, T. A., Valiant, G.A. and Frederick, E.C.
(1987) Groucho
running. Journal of Applied Physiology 62:
2326- 2337.
Anderson,T. (1996). Biomechanics and
running economy. Sports
Med, 22(2), 76-89.
Andreasson,G., Lindenberger,U., Renstrom,P.,
& Peterson,L.
(1986). Torque developed at simulated
sliding between sport shoes
and an artificial turf. Am J Sports
Med, 14(3), 225-230.
Arendt,E., & Dick,R. (1995). Knee
injury patterns among men and
women in collegiate basketball and soccer.
NCAA data and review
of literature. Am J Sports Med,
23(6), 694-701.
Bahniuk,E., & Zamir,I. (1976). Characteristics
of antifriction devices
used for ski bindings. Orthop.Clin.North
Am., 7 (1), 105-115.
Barrett,R.S., Neal,R.J., & Roberts,L.J.
(1998). The dynamic loading
response of surfaces encountered in beach
running. J Sci Med
Sport, 1(1), 1-11.
Bassey,E.J., Littlewood,J.J., & Taylor,S.J.
(1997). Relations
between compressive axial forces in an instrumented
massive
femoral implant, ground reaction forces, and
integrated
electromyographs from vastus lateralis during
various 'osteogenic'
exercises. J Biomech, 30(3), 213-223.
Bednarczyk,J.H., & Sanderson,D.J. (1994).
Kinematics of
wheelchair propulsion in adults and children
with spinal cord injury.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil, 75(12), 1327-1334.
Blickhan,R. (1989). The spring-mass model
for running and
hopping. J Biomech, 22(11-12),
1217-1227.
Bobbert,M.F., Schamhardt,H.C., & Nigg,B.M.
(1991). Calculation of
vertical ground reaction force estimates during
running from
positional data. J Biomech, 24(12),
1095-1105.
Bobbert,M.F., Yeadon,M.R., & Nigg,B.M.
(1992). Mechanical
analysis of the landing phase in heel-toe
running. J Biomech, 25(3),
223-234.
Bodnar,J. (1987). Sports Surfaces: The
Right Stuff Underfoot.
Construction Specifier, v 40(n 6), 110-112,
114, 116.
Bonstingl,R.W., Morehouse,C.A., & Niebel,B.W.
(1975). Torques
developed by different types of shoes on various
playing surfaces.
Med Sci Sports, 7(2), 127-131.
Bosco,C., Saggini,R., & Viru,A. (1997).
The influence of different
floor stiffness on mechanical efficiency of
leg extensor muscle.
Ergonomics, 40(6), 670-679.
Bowers,K.D.J., & Martin,R.B. (1975).
Cleat-surface friction on new
and old AstroTurf. Med Sci Sports,
7(2), 132-135.
Bowers,K.D.J., & Martin,R.B. (1976).
Turf-toe: a shoe-surface
related football injury. Med Sci Sports,
8(2), 81-83.
Bowers, K.D. and Martin, R.B. (1974) Impact
absorption, new and
old Astroturf at West Virginia University.
Med Sci Sports Ex.
6:217-221.
Briss,P.A., Sacks,J.J., Addiss,D.G., Kresnow,M.,
& O'Neil,J.
(1994). A nationwide study of the risk
of injury associated with day
care center attendance [see comments].
Pediatrics, 93(3),
364-368.
Briss,P.A., Sacks,J.J., Addiss,D.G., Kresnow,M.J.,
& O'Neil,J.
(1995). Injuries from falls on playgrounds.
Effects of day care center
regulation and enforcement. Arch Pediatr
Adolesc Med, 149(8),
906-911.
Brown,M., Rudicel,S., & Esquenazi,A. (1996).
Measurement of
dynamic pressures at the shoe-foot interface
during normal walking
with various foot orthoses using the FSCAN
system. Foot Ankle Int,
17(3), 152-156.
Brown,R.P. (1982). Specifications And
Tests For Artificial Sports
Surfaces. Polymer Testing, v 3(n
2), 85-98.
Brown,R.P. (1987). Performance Tests
For Artificial Sports
Surfaces. Polymer Testing, v 7(n
4), 279-292.
Buczek,F.L., & Cavanagh,P.R. (1990).
Stance phase knee and
ankle kinematics and kinetics during level
and downhill running. Med
Sci Sports Exerc, 22(5), 669-677.
Buttermann,G.R., Janevic,J.T., Lewis,J.L.,
Lindquist,C.M.,
Wood,K.B., & Schendel,M.J. (1994).
Description and application of
instrumented staples for measuring in vivo
bone strain. J Biomech,
27(8), 1087-1094.
Bylak,J., & Hutchinson,M.R. (1998).
Common sports injuries in
young tennis players. Sports Med.,
26(2), 119-132.
Chaffin,D.B., Woldstad,J.C., & Trujillo,A.
(1992). Floor/shoe slip
resistance measurement. Am Ind Hyg Assoc
J, 53(5), 283-289.
Chapman,A.E., Lonergan,R., & Caldwell,G.E.
(1984). Kinetic
sources of lower-limb angular displacement
in the recovery phase of
sprinting. Med Sci Sports Exerc,
16(4), 382-388.
Chapman,A.E., Leyland,A.J., Ross,S.M., &
Ryall,M. (1991). Effect
of floor conditions upon frictional characteristics
of squash court
shoes. J Sports Sci, 9(1), 33-41.
Charteris,J. (1998). Comparison
of the effects of backpack loading
and of walking speed on foot-floor contact
patterns. Ergonomics,
41(12), 1792-1809.
Chen,H. Relationship between plantar
pressure distribution under
the foot and insole comfort. Clinical
Biomechanics 9 6 Nov 1994,
19944.(CLBIEW,)
Chesney,D.A. (1996). Preliminary
test method for the determination
of surface firmness. IEEE Transactions
on Rehabilitation
Engineering v 4 n 3 Sep 1996, 4(3),
182-187, ISSN.
Chiu,J., & Robinovitch,S.N. (1998).
Prediction of upper extremity
impact forces during falls on the outstretched
hand [In Process
Citation]. J Biomech, 31(12),
1169-1176.
Clanton,C., Kobluk,C., Robinson,R.A., &
Gordon,B. (1991).
Monitoring surface conditions of a Thoroughbred
racetrack.
J.Am.Vet.Med.Assoc., 198(4), 613-620.
Clement,D.B., & Taunton,J.E. (1981).
A guide to the prevention of
running injuries. Aust Fam Physician,
10(3), 156-4.
Coker,T.P., Arnold,J.A., & Weber,D.L. (1978).
Traumatic lesions of
the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great
toe in athletes.
Am.J.Sports Med., 6(6), 326-334.
Colbeck,S.C. (1994). A review of
the friction of snow skis. J
Sports Sci, 12(3), 285-295.
Colbeck,S.C. (1995). Electrical
charging of skis gliding on snow.
Med Sci Sports Exerc, 27(1), 136-141.
Creagh,U., Reilly,T., & Lees,A. (1998).
Kinematics of running on
'off-road' terrain. Ergonomics,
41(7), 1029-1033.
Creagh,U., & Reilly,T. (1998). Training
and injuries amongst elite
female orienteers. J.Sports Med.Phys.Fitness,
38(1), 75-79.
Davis,B.L., & Cavanagh,P.R. (1993).
Simulating reduced gravity: a
review of biomechanical issues pertaining
to human locomotion.
Aviat Space Environ Med, 64(6), 557-566.
de Koning,J.J., de Groot,G., & van Ingen,S.
(1992). Ice friction
during speed skating. J Biomech,
25(6), 565-571.
de Koning,J.J., Nigg,B.M., & Gerritsen,K.G.
(1997). Assessment of
the mechanical properties of area-elastic
sport surfaces with video
analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc,
29(12), 1664-1668.
Dufek,J.S., & Bates,B.T. (1991).
Biomechanical factors associated
with injury during landing in jump sports.
Sports Med, 12(5),
326-337.
Ekstrand,J., & Nigg,B.M. (1989).
Surface-related injuries in soccer.
Sports Med, 8(1), 56-62.
Feehery,R.V., Jr. (1986). The biomechanics
of running on different
surfaces. Clin.Podiatr.Med.Surg.,
3(4), 649-659.
Fendley,A. (1995). Development of an
athlete/shoe/surface-related
injury prediction model for American football.
Part 1: systematic
identification of qualitative and quantitative
variables. Southern
Biomedical Engineering Conference - Proceedings
1995,
(Biomedical), 150-153, Coden.
Ferris,D.P., Louie,M., & Farley,C.T. (1998).
Running in the real
world: adjusting leg stiffness for different
surfaces. Proc R Soc
Lond B Biol Sci, 265(1400), 989-994.
Flynn,T.W., Canavan,P.K., Cavanagh,P.R., &
Chiang,J.H. (1997).
Plantar pressure reduction in an incremental
weight-bearing system.
Phys Ther, 77(4), 410-416.
Frederick,E.C. (1986). Kinematically
mediated effects of sport
shoe design: a review. J Sports Sci,
4(3), 169-184.
Fukuda H. (1988) Biomechanical analysis of
landing on surfaces with
different stiffnesses. Biomechanics XI-B (Edited
by de Groot, G.,
Hollander, A. P., Huijing, P. A. and van Ingen
Schenau, G. J.), pp
679-684. Free University Press, Amsterdam.
Gatto,F., Swannell,P., & Neal,R. (1992).
A force-indentation
relationship for gymnastic mats. J Biomech
Eng, 114(3), 338-345.
Gehlsen,G.M., Stewart,L.B., Van Nelson,C.,
& Bratz,J.S. (1989).
Knee kinematics: the effects of running on
cambers. Med Sci
Sports Exerc, 21(4), 463-466.
Gerritsen,K.G., van den Bogert,A.J., &
Nigg,B.M. (1995). Direct
dynamics simulation of the impact phase in
heel-toe running. J
Biomech, 28(6), 661-668.
Glaister,D.H. (1978). Human tolerance
to impact acceleration.
Injury, 9(3), 191-198.
Greene,P.R., & McMahon,T.A. (1979).
Running in circles.
Physiologist, 22(6), S35-S36
Greene,P.R. (1985). Running on flat turns:
experiments, theory, and
applications. J Biomech Eng,
107(2), 96-103.
Gross,T.S., & Nelson,R.C. (1988).
The shock attenuation role of the
ankle during landing from a vertical jump.
Med Sci Sports Exerc,
20(5), 506-514.
Gross,T.S., & Bunch,R.P. (1989).
Discrete normal plantar stress
variations with running speed. J Biomech,
22(6-7), 699-703.
Gross,T.S., & Bunch,R.P. (1989).
Material moderation of plantar
impact stress [see comments]. Med Sci
Sports Exerc, 21 (5),
619-624.
Heidt,R.S.J., Dormer,S.G., Cawley,P.W., Scranton,P.E.J.,
Losse,G., & Howard,M. (1996). Differences
in friction and torsional
resistance in athletic shoe-turf surface interfaces.
Am J Sports Med,
24(6), 834-842.
Heudorf,U. (1993). [Handling of red silica
gravel on sports, play and
resort surfaces with special reference to
new toxicologic results].
Gesundheitswesen, 55(10), 521-526.
Iversen,J.R., & McMahon,T.A. (1992).
Running on an incline. J
Biomech Eng, 114(4), 435-441.
Jorgensen,U. (1990). Body load
in heel-strike running: the effect of
a firm heel counter. Am J Sports Med,
18(2), 177-181.
Keene,J.S., Narechania,R.G., Sachtjen,K.M.,
& Clancy,W.G.
(1980). artan Turf on trial. A comparison
of intercollegiate football
injuries occurring on natural grass and Tartan
Turf. Am.J.Sports
Med., 8(1), 43-47.
Keller,C.S., Noyes,F.R., & Buncher,C.R.
(1987). The medical
aspects of soccer injury epidemiology.
Am.J.Sports Med., 15(3),
230-237.
Khosravi-Sichani,B., Hemami,H., & Yurkovich,S.
(1992). Energy
transformations in human movement by contact.
J Biomech, 25(8),
881-889.
Kibler,W.B. (1993). Injuries in adolescent
and preadolescent soccer
players. Med.Sci.Sports Exerc.,
25(12), 1330-1332.
King,A.I. (1993). Progress of research
on impact biomechanics. J
Biomech Eng, 115(4B), 582-587.
Komi,P.V., Gollhofer,A., Schmidtbleicher,D.,
& Frick,U. (1987).
Interaction between man and shoe in running:
considerations for a
more comprehensive measurement approach.
Int J Sports Med,
8(3), 196-202.
Krahenbuhl, G.S. (1974) Speed of movement with
varying footwear
conditions on synthetic turf and natural grass.
Research Quarterly
45:28-33.
Lafortune,M.A., Henning,E., & Valiant,G.A.
(1995). Tibial shock
measured with bone and skin mounted transducers.
J Biomech,
28(8), 989-993.
Langley,J., & Crosado,B. (1984).
Two safety aspects of public
playground climbing equipment. N Z Med
J, 97(758), 404-406.
Leach,D.H., & Dagg,A.I. (1983). A
review of research on equine
locomotion and biomechanics. Equine
Vet J, 15(2), 93-102.
Lees,A., & Nolan,L. (1998). The biomechanics
of soccer: a review.
J Sports Sci, 16(3), 211-234.
Lehman,R.C. (1988). Surface and equipment
variables in tennis
injuries. Clin.Sports Med., 7(2),
229-232.
Lejeune,T.M., Willems,P.A., & Heglund,N.C.
(1998). Mechanics and energetics of human locomotion on sand.
J Exp Biol, 201 ( Pt 13),
2071-2080.
Levy,I.M., Skovron,M.L., & Agel,J. (1990).
Living with artificial
grass: a knowledge update. Part 1: Basic science.
Am.J.Sports
Med., 18(4), 406-412.
Lewis,L.M., Naunheim,R., Standeven,J., &
Naunheim,K.S. (1993).
Quantitation of impact attenuation of different
playground surfaces
under various environmental conditions using
a tri-axial
accelerometer. J Trauma, 35(6),
932-935.
Lillis,K.A., & Jaffe,D.M. (1997).
Playground injuries in children.
Pediatr Emerg Care, 13(2), 149-153.
Lord,M., Hosein,R., & Williams,R.B. (1992).
Method for in-shoe
shear stress measurement. J Biomed Eng,
14(3), 181-186.
Louie,J.K., Kuo,C.Y., Gutierrez,M.D., &
Mote,C.D.J. (1984).
Surface EMG and torsion measurements during
snow skiing:
laboratory and field tests. J Biomech,
17(10), 713-724.
Mack,M.G., Hudson,S., & Thompson,D. (1997).
A descriptive
analysis of children's playground injuries
in the United States
1990-4. Inj Prev, 3(2),
100-103.
Majid,F., & Bader,D.L. (1993). A
biomechanical analysis of the
plantar surface of soccer shoes. Proc
Inst Mech Eng [H], 207(2),
93-101.
Martin,R.B., Liptai,L., Yerby,S., & Williams,K.R.
(1994). The
relationship between mass and acceleration
for impacts on padded
surfaces [see comments]. J.Biomech.,
27(3), 361-364.
Mavin,K.C. (1985). Slip Resistance Of
Footways And Sporting
Surfaces. National Conference Publication
- Institution of
Engineers, Australia, (n 85/14), 245-249.
McCullagh,P.J., & Graham,I.D. (1985).
A preliminary investigation
into the nature of shock absorbency in synthetic
sports materials. J
Sports Sci, 3(2), 103-114.
McGill,S.M. (1992). A myoelectrically
based dynamic
three-dimensional model to predict loads on
lumbar spine tissues
during lateral bending. J Biomech,
25(4), 395-414.
McKenzie,D.C., Clement,D.B., & Taunton,J.E.
(1985). Running
shoes, orthotics, and injuries. Sports
Med, 2(5), 334-347.
McMahon,T.A. (1975). Using body
size to understand the structural
design of animals: quadrupedal locomotion.
J Appl Physiol, 39(4),
619-627.
McMahon,T.A. (1979). Gravitational
scale effects. Physiologist,
22(6), S5-S6
McMahon, T. A. and Greene, P. R. (1978) Fast
running tracks.
Scientific American 239:148-163.
McMahon, T. A. and Greene, P. R. (1979) The
influence of track
compliance on running. J. Biomech 12:893-904.
McMahon,T.A. (1987). Biomechanics. The spring in the human foot [news]. Nature, 325(7000), 108-109.
McMahon,T.A., & Cheng,G.C. (1990).
The mechanics of running:
how does stiffness couple with speed?
J Biomech, 23 Suppl 1,
65-78.
Memari,A.M. (1994). Linear and nonlinear
finite element study of
polyurethane used in sports shoes. Advances
in Structural
Engineering Computing International Conference
on Computational
Structures Technology - Proceedings 1994,
(Structural), Limited,
Edinburgh, Scotl-87, Coden.
Menck,H., & Jorgensen,U. (1983).
Frictional forces and ankle
fractures in sport. Br J Sports Med,
17(4), 135-136.
Metzl,J.D. (1999). Sports-specific concerns
in the young athlete:
football [In Process Citation]. Pediatr.Emerg.Care,
15(5), 363-367.
Mikic,B., & Carter,D.R. (1995). Bone
strain gage data and
theoretical models of functional adaptation.
J Biomech, 28(4),
465-469.
Milburn,P.D., & Barry,E.B. (1998).
Shoe-surface interaction and the
reduction of injury in rugby union.
Sports Med, 25 (5), 319-327.
Mizrahi,J., & Susak,Z. (1982). In-vivo
elastic and damping response
of the human leg to impact forces. J
Biomech Eng, 104(1), 63-66.
Mott,A., Evans,R., Rolfe,K., Potter,D., Kemp,K.W.,
& Sibert,J.R.
(1994). Patterns of injuries to children
on public playgrounds. Arch
Dis Child, 71(4), 328-330.
Mott,A., Rolfe,K., James,R., Evans,R., Kemp,A.,
Dunstan,F.,
Kemp,K., & Sibert,J. (1997). Safety
of surfaces and equipment for
children in playgrounds. Lancet,
349(9069), 1874-1876.
Myers,M.J., Steudel,K., & White,S.C. (1993).
Uncoupling the
correlates of locomotor costs: a factorial
approach. J Exp Zool,
265(3), 211-223.
Nicholas,J.A., Rosenthal,P.P., & Gleim,G.W.
(1988). A historical
perspective of injuries in professional football.
Twenty- six years of
game-related events. JAMA, 260(7),
939-944.
Nigg,B.M. (1985). Biomechanics, load
analysis and sports injuries in
the lower extremities. Sports
Med., 2(5), 367-379.
Nigg,B.M., & Yeadon,M.R. (1987).
Assessment Of Vertical Surface
Deformation Of Area Elastic Sport. American
Society of
Mechanical Engineers, Design Engineering Division
(Publication)
DE, v 13, 17
Nigg,B.M., & Yeadon,M.R. (1987).
Biomechanical aspects of
playing surfaces. J Sports Sci,
5(2), 117-145.
Nigg,B.M., & Segesser,B. (1988).
The influence of playing surfaces
on the load on the locomotor system and on
football and tennis
injuries. Sports Med, 5(6),
375-385.
Nigg,B.M., Yeadon,M.R., & Herzog,W. (1988).
The influence of
construction strategies of sprung surfaces
on deformation during
vertical jumps. Med Sci Sports Exerc,
20(4), 396-402.
Nigg,B.M. (1990). The validity and relevance
of tests used for the
assessment of sports surfaces. Med Sci
Sports Exerc, 22(1),
131-139.
Nigg,B.M., De Boer,R.W., & Fisher,V. (1995).
A kinematic
comparison of overground and treadmill running.
Med Sci Sports
Exerc, 27(1), 98-105.
Nigg,B.M., & Anton,M. (1995). Energy
aspects for elastic and
viscous shoe soles and playing surfaces.
Med Sci Sports Exerc,
27(1), 92-97.
Nigg,B.M., Luethi,S., Denoth,J., & Stacoff,A.
(1983).
Methodological Aspects Of Sport Shoe And Sport
Surface
Analysis. Biomechanics In Sport - A
1987 Update International
Series on Biomechanics, v 4B, 1041-1052.
Nilsson,J., Thorstensson,A., & Halbertsma,J.
(1985). Changes in
leg movements and muscle activity with speed
of locomotion and
mode of progression in humans.
Acta Physiol Scand, 123(4),
457-475.
Novick,A., Stone,J., Birke,J.A., Brasseaux,D.M.,
Broussard,J.B.,
Hoard,A.S., & Hawkins,E.S. (1993).
Reduction of plantar pressure
with the rigid relief orthosis. J Am
Podiatr Med Assoc, 83(3),
115-122.
Oberg,B., Moller,M., Gillquist,J., & Ekstrand,J.
(1986). Isokinetic
torque levels for knee extensors and knee
flexors in soccer players.
Int J Sports Med, 7(1), 50-53.
Oggero,E., Pagnacco,G., Morr,D.R., Barnes,S.Z.,
& Berme,N.
(1997). The mechanics of drop landing
on a flat surface--a
preliminary study. Biomed Sci Instrum,
33, 53-58.
Ozguven,H.N., & Berme,N. (1988).
An experimental and analytical
study of impact forces during human jumping.
J Biomech, 21(12),
1061-1066.
Powell,J.W., & Schootman,M. (1992).
A multivariate risk analysis of
selected playing surfaces in the National
Football League: 1980 to
1989. An epidemiologic study of knee injuries.
Am.J.Sports Med.,
20(6), 686-694.
Recuero,A. (1995). Uneven dynamic response
of floors in a sports
pavilion. Computers and Structures v
55 n 1 Apr 3 1995, 55(1),
185-189, ISSN.
Redfern,M.S., Moore,P.L., & Yarsky,C.M.
(1997). The influence of
flooring on standing balance among older persons.
Hum Factors,
39(3), 445-455.
Rheinstein,D.J., Morehouse,C.A., & Niebel,B.W.
(1978). Effects on
traction of outsole composition and hardnesses
of basketball shoes
and three types of playing surfaces.
Med Sci Sports, 10(4),
282-288.
Robbins,S.E., Hanna,A.M., & Gouw,G.J. (1988).
Overload
protection: avoidance response to heavy plantar
surface loading.
Med Sci Sports Exerc, 20(1), 85-92.
Robbins,S.E., Gouw,G.J., & Hanna,A.M. (1989).
Running-related
injury prevention through innate impact-moderating
behavior. Med
Sci Sports Exerc, 21(2), 130-139.
Robinovitch,S.N., Hayes,W.C., & McMahon,T.A.
(1997). Predicting
the impact response of a nonlinear single-degree-of-freedom
shock-absorbing system from the measured step
response. J
Biomech Eng, 119 (3), 221-227.
Robinovitch,S.N., & Chiu,J. (1998).
Surface stiffness affects impact
force during a fall on the outstretched hand.
J Orthop Res, 16(3),
309-313.
Rodeo,S.A., O'Brien,S., Warren,R.F., Barnes,R.,
Wickiewicz,T.L., &
Dillingham,M.F. (1990). Turf-toe: an
analysis of
metatarsophalangeal joint sprains in professional
football players.
Am J Sports Med, 18(3), 280-285.
Sands,W.A., Hondzinski,J.M., Shultz,B.B., &
George,G.S. (1995). A
comparison of subtalar joint maximal eversion
while jogging on the
minitrampoline and floor. J Orthop Sports
Phys Ther, 22(2), 65-72.
Savageau,M.A. (1985). Mathematics
of organizationally complex
systems. Biomed.Biochim.Acta,
44(6), 839-844.
Schweizer,L. Testing Procedures for Landing
Mats, Surfaces for
Floor Exercises and Vaulting Boards. (1985).
Anonymous. Institute
for Sport and Sport Science, University of
Freiburg, Freiburg,
Germany: International Gymnastics Federation.
Scott,S.H., & Winter,D.A. (1993).
Biomechanical model of the
human foot: kinematics and kinetics during
the stance phase of
walking. J Biomech, 26(9), 1091-1104.
Scranton,P.E.J., Whitesel,J.P., Powell,J.W.,
Dormer,S.G.,
Heidt,R.S.J., Losse,G., & Cawley,P.W.
(1997). A review of selected
noncontact anterior cruciate ligament injuries
in the National Football
League. Foot Ankle Int, 18(12),
772-776.
Shaw,J.E., Hsi,W.L., Ulbrecht,J.S., Norkitis,A.,
Becker,M.B., &
Cavanagh,P.R. (1997). The mechanism
of plantar unloading in total
contact casts: implications for design and
clinical use. Foot Ankle
Int, 18(12), 809-817.
Shiffer,R.C. (1994). ASTM F-1292
as a tool for playground injury
severity reduction. ASTM Special Technical
Publication n 1229
1994, (n), 340-345, ISSN.
Skovron,M.L., Levy,I.M., & Agel,J. (1990).
Living with artificial
grass: a knowledge update. Part 2: Epidemiology.
Am.J.Sports
Med., 18(5), 510-513.
Sosin,D.M., Keller,P., Sacks,J.J., Kresnow,M.,
& van Dyck,P.C.
(1993). Surface-specific fall injury
rates on Utah school
playgrounds. Am J Public Health,
83(5), 733-735.
Stanitski,C.L. (1989). Common injuries
in preadolescent and
adolescent athletes. Recommendations for prevention.
Sports
Med., 7(1), 32-41.
Steele,J.R. (1990). Biomechanical factors
affecting performance in
netball. Implications for improving performance
and injury reduction.
Sports Med., 10(2), 88-102.
Sun,J., Walters,M., Svensson,N., & Lloyd,D.
(1996). The influence
of surface slope on human gait characteristics:
a study of urban
pedestrians walking on an inclined surface.
Ergonomics, 39(4),
677-692.
Tang,P.F., & Woollacott,M.H. (1998).
Inefficient postural responses
to unexpected slips during walking in older
adults. J Gerontol A Biol
Sci Med Sci, 53(6), M471-M480
Tomaro,J., & Burdett,R.G. (1993).
The effects of foot orthotics on
the EMG activity of selected leg muscles during
gait. J Orthop
Sports Phys Ther, 18(4), 532-536.
Torg,J.S., Stilwell,G., & Rogers,K. (1996).
The effect of ambient
temperature on the shoe-surface interface
release coefficient. Am J
Sports Med, 24(1), 79-82.
Valiant,G. (1999). The effect of outsole
pattern on basketball shoe
traction. Proceedings of ISBS: Biomechanics
in Sports III & !V,
29-37.
van den Kroonenberg,A.J., Hayes,W.C., &
McMahon,T.A. (1995).
Dynamic models for sideways falls from standing
height. J Biomech
Eng, 117(3), 309-318.
van den,B.A., Read,L., & Nigg,B.M. (1996).
A method for inverse
dynamic analysis using accelerometry.
J.Biomech., 29(7), 949-954.
van Weperen,W. (1991). Overall
approach to the safety of
playgrounds. Building and Environment
Use and Safety Safety
Science v 14 n 2 Aug 1991, 14(2), 103-108,
ISSN.
Veeger,D., van der Woude,L.H., & Rozendal,R.H.
(1989). The
effect of rear wheel camber in manual wheelchair
propulsion. J
Rehabil Res Dev, 26(2), 37-46.
Viitasalo,J.T., Hamalainen,K., Mononen,H.V., Salo,A., & Lahtinen,J. (1993). Biomechanical effects of fatigue during continuous hurdle jumping. J Sports Sci, 11(6), 503-509.
Wenger,W., & McIlhagger,R. (1992).
Surface-finish characteristics
of composite components. J Mater Process
Technol v 33 n 4 Sep
1992 p 439-452, ISSN 0924-0136, Coden JMPTEF,
JA (Journal
Article), 33 (4), 439-452, ISSN.
Werner,P. (1982). Playground injuries
and voluntary product
standards for home and public playgrounds.
Pediatrics, 69(1),
18-20.
Wilson,D.R., Neal,R.J., & Swannell,P. (1989).
The response of
gymnastic sports floors to dyanmic loading.
Austrailian Journal of
Science and Medicine in Sport, 21(1),
14-19.
Yeadon,M.R., & Nigg,B.M. (1988).
A method for the assessment of
area-elastic surfaces. Med Sci Sports
Exerc, 20(4), 403-407.
Zebarth,B.J., & Sheard,R.W. (1985).
Impact and shear resistance of
turf grass racing surfaces for Thoroughbreds.
Am.J.Vet.Res.,
46(4), 778-784.
Disagree? Please email me!  kirtleymd@yahoo.com
kirtleymd@yahoo.com