 Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis
Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis
 History of gait analysis
History of gait analysis
-
If a man were to walk on the ground alongside a wall with a reed dipped
in ink attached to his head, the line traced by the reed would not be straight
but zigzag, because it goes lower when he bends and higher when he stands
upright
Aristotle (384-322 BC)
-
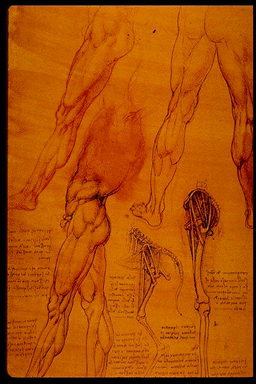
Leonardo da Vinci (1452-1519)
-
Giovanni Borelli (1608-79)
-
Weber brothers (1836)
-
du Bois-Raymond (1849): Electromyography
-
Duchenne (1855)
-
Eadweard Muybridge
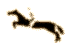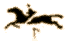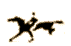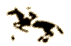

-
Leland Stanford, Governor of California, asked him to photograph his famous
horse, Occident, to find out whether a trotting horse ever had all four
feet off the ground (Sacramento 1872) ground at any one point in time
-
20,000 photographs of men, women, children, animals & birds in motion
(Palo Alto, 1878-1879)
-
"Attitudes of Animals in Motion" (1881)


 Animated
by Charl
Lucasson
Animated
by Charl
Lucasson
-
Animal Locomotion (1887)
-
The Human Figure in Motion" (1901)
-
Gave rise to the invention of cinema
-
Braune & Fischer (1895): classic scientific study of human gait: body
& joint forces calculated
-
Bernstein (1935): studies in Russia
-
Elftmann (1938): mechanical force platforms
-
Murray (1964): Walking patterns of normal men
-
Paul (1966): Hip joint forces in normal walking
-
Winter (1978): TV system, Joint powers
 Why do we need to do computerised
motion analysis?
Why do we need to do computerised
motion analysis?
-
eye is too slow (flicker-fusion rate about 12 Hz)
-
motion leaves no record
-
to analyse internal forces and moments (torques)
 Uses
Uses
-
diagnosis
-
monitoring (before/after treatment)

Orthoses Surgery
Botox
-
documentation
-
research
 Types of measurement systems
Types of measurement systems
-
electro-goniometers (e.g. Penny & Giles)
-
electro-magnetic (e.g. Polhemus Flock of Birds, Ascension Motion Tracker)
-
cine film
-
video
-
visual light (e.g. Peak)

-
infra-red
-
passive markers (e.g. Vicon, Motion Analysis Corp., Elite)
-
active markers (e.g. CODA, Optotrak, Selspot)
 Video systems
Video systems
-
charge-coupled device cameras
-
fast shutter-speed (1/500 s or less)
-
retro-reflective markers
-
one camera for 2D, several (e.g. 6) for 3D
 Force Platforms
Force Platforms 
-
Joint reaction forces and moments can be calculated from kinematics
(Inverse Dynamics)

-
During stance phase, foot is in contact with ground, so need to measure
ground reaction
-
Force platform measures 6 components (3 forces, 3 moments) of the vector:
-
Problems in hitting platform
-
targetting
-
short step-length
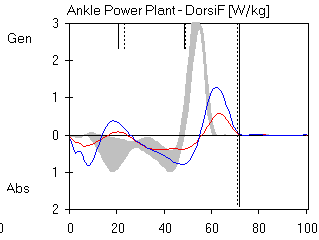
 Interpretation:
Five common abnormalities
Interpretation:
Five common abnormalities
-
Inadequate push-off & step-length
 Electromyography
Electromyography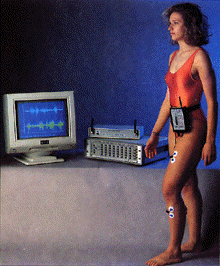
-
Surface electrodes - fine wire for peroneii

-
Filtering
-
Problems of noise, interpretation

 Laboratory
Laboratory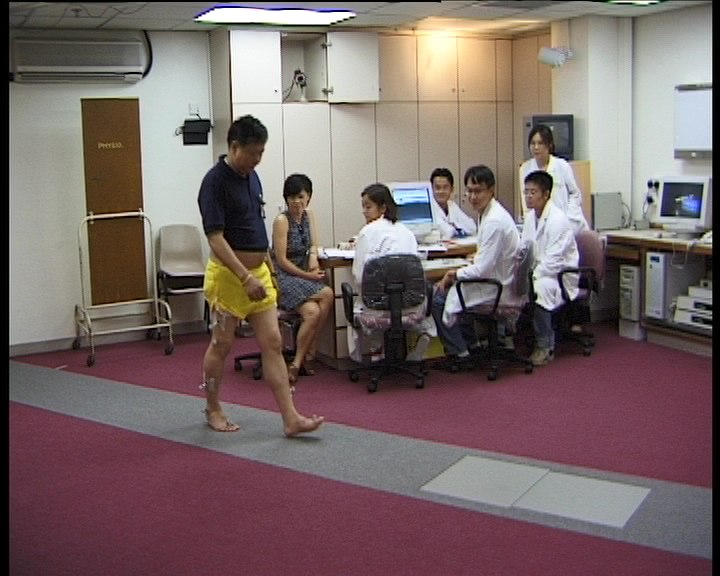 
-
Capture normal gait with Vicon 370 motion analysis system
-
Analyse with Vicon Clinical Manager
 The Vicon Clinical Manager
Marker Set
The Vicon Clinical Manager
Marker Set
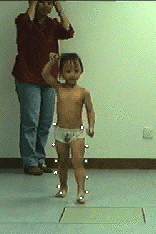
-
13 markers
-
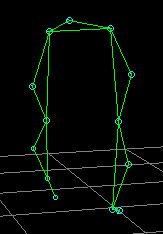
Hip-joint centre estimated by anthropometry
-
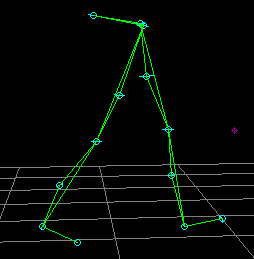
Knee-joint axis estimated clinically (femoral condyle)
-
antero-posterior errors result in flexion-offset
-
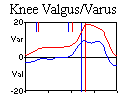
rotational errors result in knee varus/valgus artifact
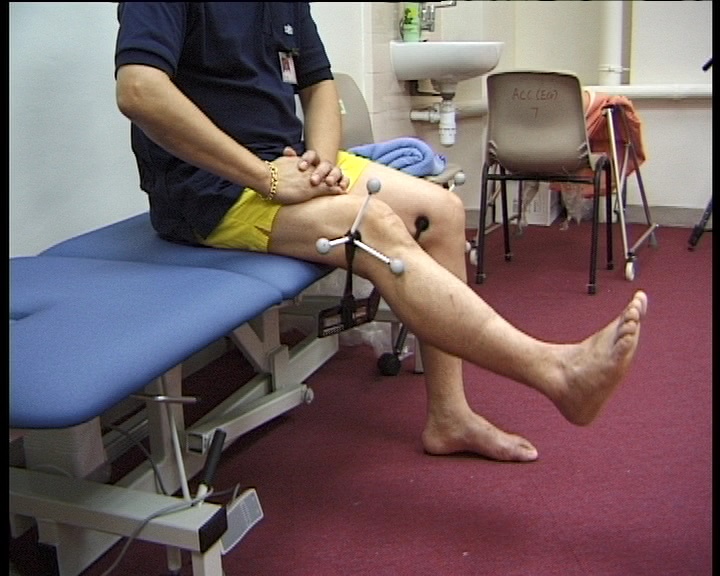
-
Ankle-joint axis assumed to be at lateral malleolus
-
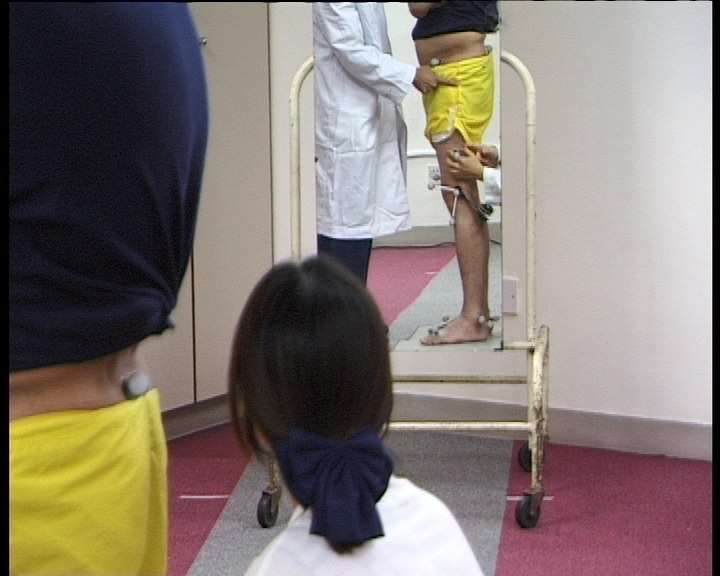 Thigh and shank wands
need to be in a straight line
Thigh and shank wands
need to be in a straight line
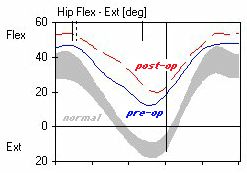
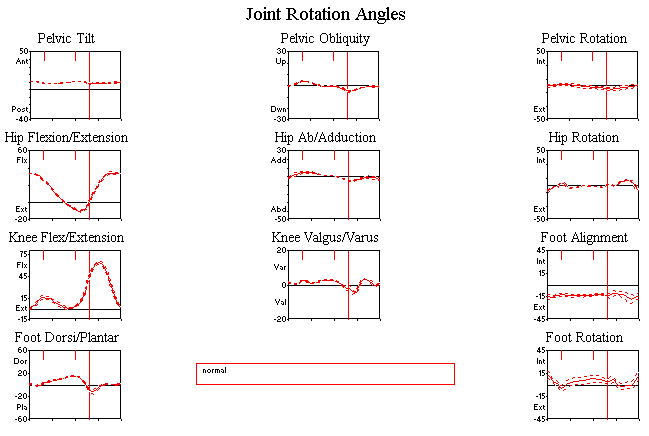
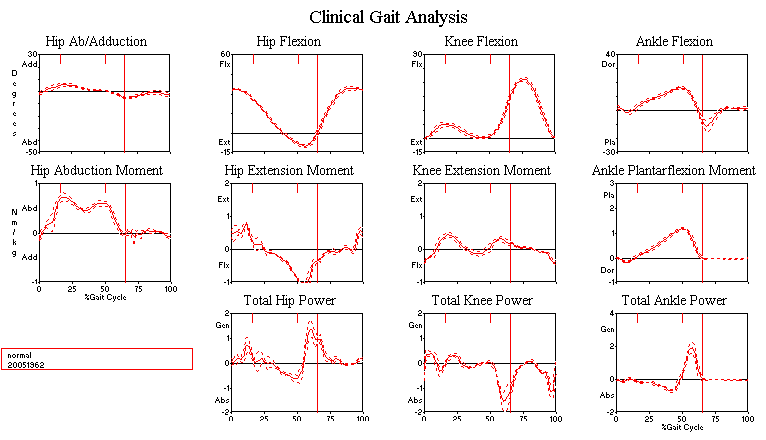
Normal Curves
 Want to know more?
Want to know more?
By Chris Kirtley MD,
PhD 

 Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis
Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis
Introduction to Computerized
Gait Analysis



 Animated
by Charl
Lucasson
Animated
by Charl
Lucasson





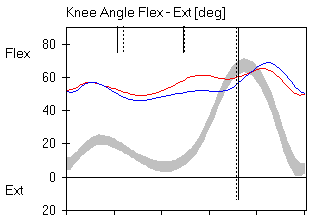
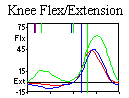 knee
pain orweak
quads
knee
pain orweak
quads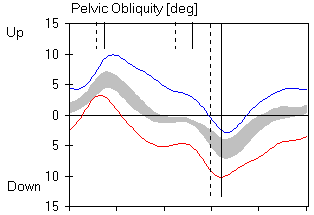










 Thigh and shank wands
need to be in a straight line
Thigh and shank wands
need to be in a straight line
